
 HanSaRam VII
HanSaRam VII
KAIST developed the seventh robot in the HanSaRam series called HanSaRam VII. It has five fingers in each hand, can grasp and release objects, and can express hand gestures.
 HanSaRam VI
HanSaRam VI
KAIST developed the sixth robot in the HanSaRam series called HanSaRam VI. It generates walking pace through 3D linear inverted pendulum mode, which makes easy to control motions.
 HanSaRam V
HanSaRam V
KAIST developed the fifth robot in the HanSaRam series called HanSaRam V. With independent locomotion, sensing and processing, it can walk in patterns avoiding obstacles.
 HanSaRam III
HanSaRam III
KAIST developed the third robot in the HanSaRam series called HanSaRam III. It has 22 DOFs and a camera for visual feedback, and can grasp objects with its claw-like hands.
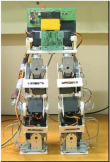 HanSaRam IV
HanSaRam IV
KAIST developed the fourth robot in the HanSaRam series called HanSaRam IV. It has 12 servomotors, 4 force sensing resistors in each foot, and master-slave controllers.
 HanSaRam II
HanSaRam II
KAIST developed the second robot in the HanSaRam series called HanSaRam II. This bipedal walking robot has the shape of a human body with different upper and lowers parts.
 HanSaRam I
HanSaRam I
KAIST developed the first robot in the HanSaRam series called HanSaRam I. This bipedal robot was created to test the walking algorithm and control method of lightweight robots.